Your mental health is just as important as your physical health—and one of the most powerful ways to improve it is through daily exercise.
Science proves that movement isn’t just for weight loss or muscle gain; it rewires your brain, reduces stress, and even fights depression.
In this guide, we’ll break down the 4 most impactful mental health benefits of exercise—backed by research—so you can start feeling better, starting today.
1. Reduces Stress & Anxiety (Faster Than You Think)
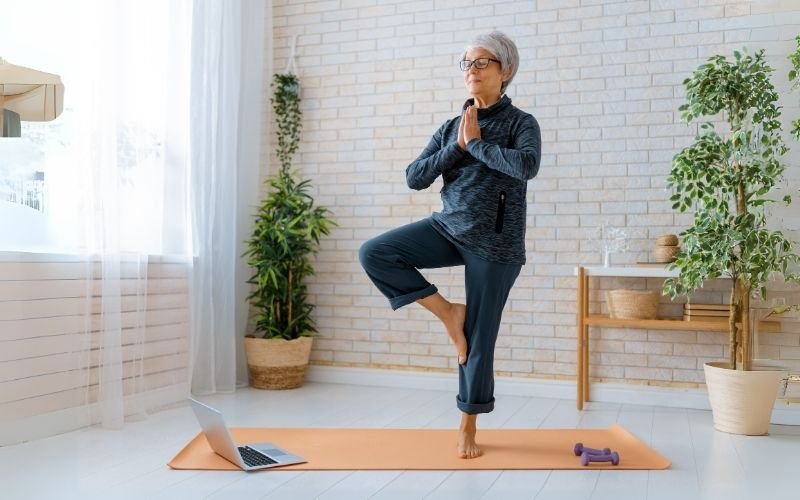

Exercise is one of the fastest ways to lower cortisol, the body’s primary stress hormone. Studies show that just 30 minutes of moderate exercise (like brisk walking or cycling) can:
- Decrease tension in muscles
- Improve relaxation by boosting endorphins
- Reduce symptoms of anxiety as effectively as therapy for some people
Best exercises for stress relief:
- Yoga (try Yoga with Adriene’s free YouTube sessions)
- Swimming or water aerobics
- Nature walks (forest bathing has proven calming effects)
For those with high-stress jobs, a heart rate monitor like the Fitbit Charge 5 can help track stress levels and recovery.
2. Boosts Mood & Fights Depression
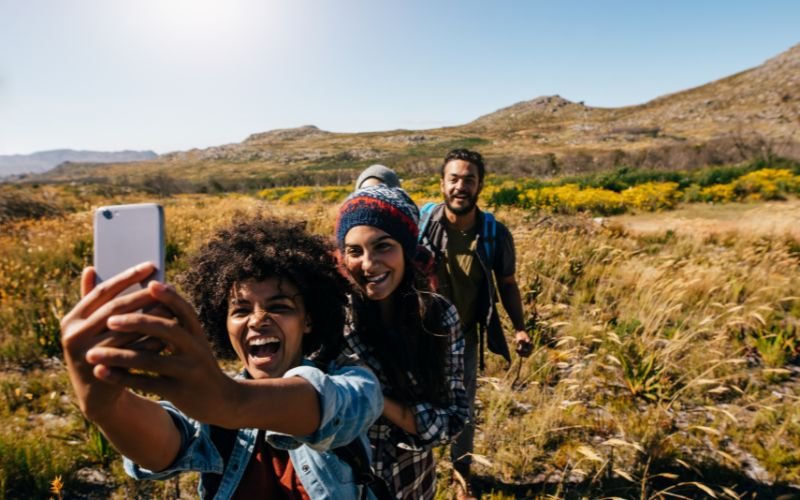

Physical activity triggers the release of serotonin, dopamine, and endorphins—your brain’s natural “feel-good” chemicals. Research shows that regular exercise can:
- Work as well as antidepressants for mild to moderate depression
- Increase self-esteem by improving body image and energy
- Prevent depressive relapses long-term
Most effective mood-boosting workouts:
- Dancing (Zumba or even freestyle at home)
- Team sports (social connection enhances the effect)
- High-intensity interval training (HIIT) for a quick endorphin rush
If motivation is a struggle, a fitness app like Nike Training Club offers guided workouts for all levels.
3. Enhances Cognitive Function & Focus
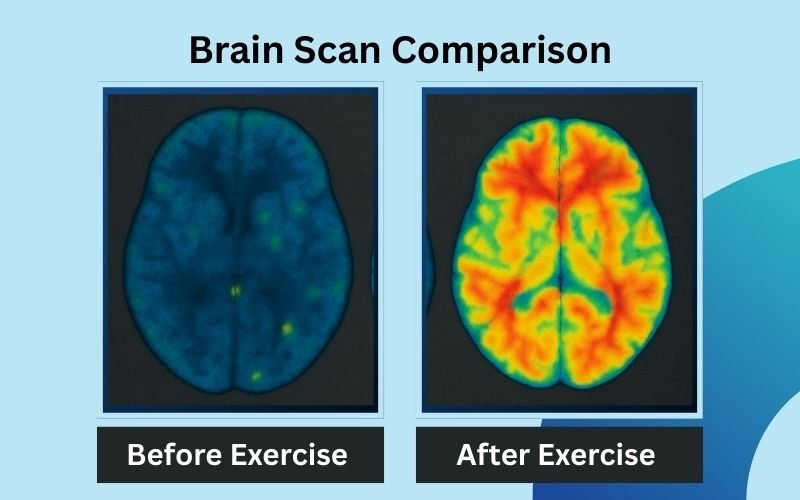
Exercise doesn’t just help your emotions—it sharpens your brain. Aerobic activity increases blood flow to the brain, which:
- Improves memory and learning (critical for students or professionals)
- Lowers risk of dementia by up to 30%
- Helps ADHD symptoms by boosting dopamine naturally
Top brain-boosting exercises:
- Running or jogging (even 20 minutes helps)
- Tai Chi (combines movement and mindfulness)
- Boxing or martial arts (enhances coordination and focus)
For tracking progress, a smartwatch like the Garmin Venu 2 can monitor how exercise impacts your focus and sleep quality.
Other Recommended Articles:
10 Deadly Sports Nutrition Mistakes Sabotaging Your Performance (Simple Fixes to Boost Your Game!)
10 Powerful and Effective Weight Loss Diets That Actually Work
4. Improves Sleep Quality (Which Fuels Mental Resilience)
Poor sleep worsens anxiety, depression, and brain fog. Exercise helps regulate your circadian rhythm, leading to:
- Deeper, more restorative sleep
- Fewer nighttime awakenings
- Reduced insomnia symptoms
Best exercises for better sleep:
- Evening yoga or stretching (avoid intense workouts before bed)
- Morning sunlight walks (sets your natural sleep-wake cycle)
- Resistance training (linked to longer sleep duration)
For those with chronic sleep issues, a weighted blanket or natural sleep aid like Olly Sleep Gummies may complement an exercise routine.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. How much exercise is needed for mental health benefits?
Just 30 minutes, 3-5 times per week shows measurable improvements. Even short 10-minute walks help.
2. What if I hate exercising?
Start small—dancing, gardening, or playing with pets counts. Consistency matters more than intensity.
3. Can exercise replace therapy or medication?
For mild cases, it can be as effective as medication. Always consult a doctor for severe mental health conditions.
4. When will I notice mood improvements?
Many feel calmer immediately after a workout. Long-term benefits build over 4-6 weeks of consistency.
Final Thoughts
Exercise isn’t just about physical fitness—it’s a proven tool for mental health that reduces stress, boosts happiness, sharpens focus, and improves sleep.
The best part? You don’t need a gym membership or hours of time. Start with 10 minutes today and build from there.
Need gear or guidance? Check out Yoga mats from Gaiam or Fitbit fitness trackers to stay motivated.




